Circular Economy Principles: Sustainable Packaging Solutions
The circular economy is a transformative production and consumption approach focusing on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency. In the packaging industry, implementing circular economy principles is crucial to reducing environmental impact and enhancing sustainability. Key strategies include packaging waste reduction, closed-loop systems, refillable and reusable packaging, and designing packaging for recyclability.
Packaging Waste Reduction Strategies

Packaging waste is a significant environmental challenge, contributing to pollution and resource depletion. Companies can adopt various strategies to reduce waste, including:
- Lightweight Packaging: Reducing the material used in packaging without compromising strength or functionality lowers material consumption and decreases transportation emissions.
- Minimalist Design: Eliminating unnecessary packaging components and excessive branding materials can significantly cut waste.
- Alternative Materials: Using biodegradable, compostable, or bio-based materials instead of conventional plastics helps minimize environmental impact.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): Brands adopting EPR policies take accountability for their packaging waste, encouraging efficient recycling and disposal programs.
- Consumer Awareness Campaigns: Educating consumers about responsible packaging disposal and encouraging sustainable choices to reduce waste generation at the source.
Closed-Loop Packaging Systems
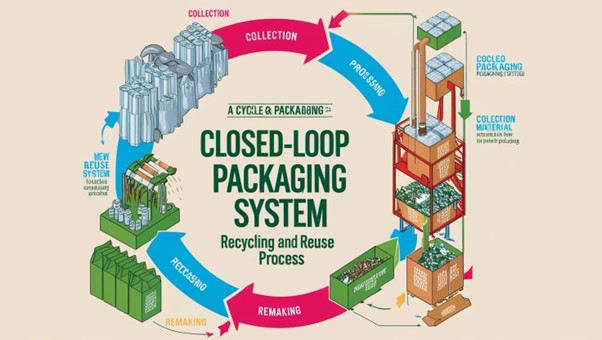
A closed-loop packaging system ensures that materials remain in circulation rather than becoming waste. This approach focuses on designing packaging that can be recovered, reused, or recycled into the system. Key aspects include:
- Reverse Logistics: Implementing efficient return and collection systems for used packaging materials, ensuring they are properly processed for reuse or recycling.
- Use of Recycled Content: Incorporating post-consumer recycled materials in packaging production minimizes reliance on virgin materials.
- Take-Back Programs: Brands offering take-back initiatives encourage consumers to return used packaging for proper recycling or reuse.
- Industrial Composting: For compostable packaging, establishing industrial composting facilities ensures proper breakdown without environmental harm.
Refillable and Reusable Packaging Solutions

Refillable and reusable packaging models significantly reduce waste by extending the life cycle of packaging materials. Some effective strategies include:
- Refill Stations: Retailers and brands introduce refill stations where customers can replenish products such as detergents, personal care items, and beverages, reducing single-use packaging waste.
- Deposit Return Schemes: Consumers return packaging (e.g., glass bottles, metal containers) for a refund, incentivizing reuse.
- Durable Packaging Materials: Using materials like glass, metal, and rigid plastics that can withstand multiple reuse cycles enhances sustainability.
- Brand-Managed Reuse Programs: Companies like Loop and Algramo provide refillable product delivery services, ensuring packaging returns to the supply chain instead of becoming waste.
Packaging Design for Recyclability

Designing packaging for recyclability ensures that materials can be efficiently processed and reintroduced into the production cycle. Best practices include:
- Mono material Packaging: Using a single material instead of multi-layered composites simplifies recycling and increases recovery rates.
- Easily Separable Components: Designing packaging with detachable components (e.g., lids, labels) allows for proper sorting and recycling.
- Recyclable Inks and Adhesives: Traditional printing inks and adhesives can hinder recycling; using eco-friendly alternatives improves material recovery.
- Clear Labeling: Providing clear recycling instructions on packaging helps consumers properly dispose of materials, preventing contamination in recycling streams.
- Standardized Packaging Materials: Aligning with widely accepted recyclable materials, such as PET, HDPE, and aluminum, ensures higher recycling success rates.
Conclusion
The circular economy presents a viable solution to the growing packaging waste crisis. By embracing waste reduction strategies, closed-loop systems, reusable models, and recyclable designs, businesses can contribute to a more sustainable future.
Consumers, businesses, and policymakers must collaborate to drive innovation, encourage responsible consumption, and establish an infrastructure that supports circular packaging solutions. Shifting towards a circular economy is an environmental necessity and an opportunity for businesses to enhance brand reputation and meet evolving consumer expectations for sustainability.
References:
https://supplychain.edf.org/resources/sustainability-101-packaging-waste-solutions/